In this post Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples , We will know about VLOOKUP formulas with some examples.
Excel is a widely used spreadsheet application that offers powerful tools to manage, analyze, and visualize data. Among these, one of the most useful and popular formulas is VLOOKUP (Vertical Lookup). Whether you are a beginner or an advanced user, mastering VLOOKUP Excel formulas with examples will help you quickly find relevant data in large datasets, saving your time and improving accuracy.
In this comprehensive guide, you will learn what VLOOKUP is, how it works, practical examples, common errors, and advanced tips to effectively use this formula in your daily Excel tasks.
What is VLOOKUP in Excel?
VLOOKUP stands for Vertical Lookup. It is used to search for a value in the first column of a table and return a corresponding value in the same row from another specified column. The function searches vertically down the first column to find the lookup value.
This formula is especially useful in large worksheets where manually finding and matching data would be time-consuming and error-prone.
The VLOOKUP Formula Syntax
The formula syntax has four parts:
VLOOKUP(lookup_value,table_array,col_index_num,[range_lookup])
- lookup_value: The value you want to find in the first column.
- table_array: The table or range of cells including the lookup column and the data to retrieve.
- col_index_num: The column number (starting from 1) in the table from which to retrieve the result.
- range_lookup: [Optional] TRUE for approximate match (default), FALSE for exact match.
How to Use Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples
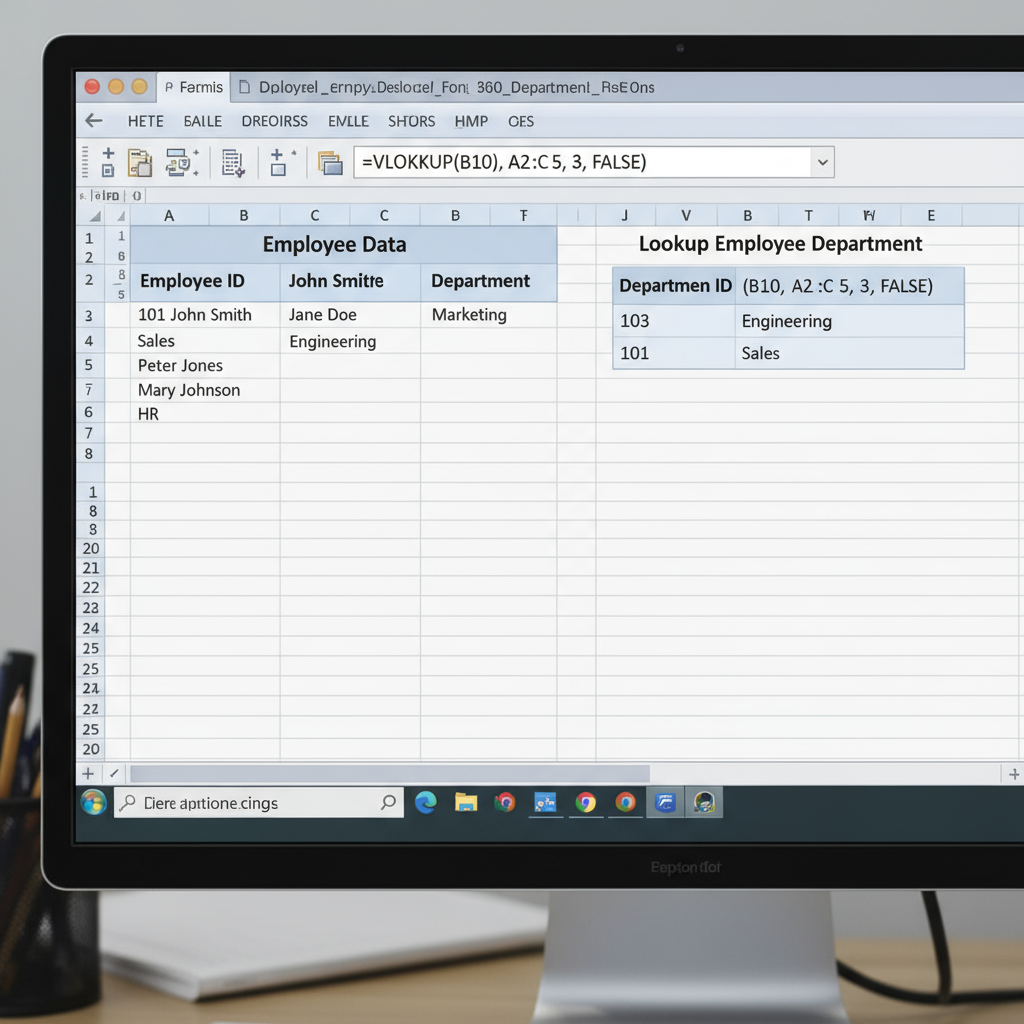
Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples1: Exact Match Lookup
| Employee ID | Name | Department |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Raj Sawant | HR |
| 102 | Deep Chandra | IT |
| 103 | Gauri Deshpande | Marketing |
| 104 | Ishita Sharma | Finance |
You want to find the department of the employee with ID 103.
Formula:
=VLOOKUP(103,A2:C5,3,FALSE)
- It looks for “103” in the first column (A2:A5).
- Returns value from the 3rd column (Department).
- Uses FALSE to find an exact match.
Result: “Marketing”
Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples 2: Using Cell Reference for Dynamic Lookup
Instead of hardcoding the lookup value, you can reference a cell. If cell E2 contains the Employee ID to search:
=VLOOKUP(E2,$A$2:$C$5,3,FALSE)
The $ signs fix the table array when copying the formula, and E2 can be changed to lookup different IDs dynamically.
Example 3: Approximate Match Lookup for Grades
Consider a grading scale:
| Min Score | Grade |
|---|---|
| 0 | F |
| 50 | D |
| 60 | C |
| 70 | B |
| 80 | A |
To find the grade for a score of 75:
=VLOOKUP(75,A2:B6,2,TRUE)
- TRUE enables approximate matching, so it finds the largest value less than or equal to 75 (which is 70).
- Returns grade “B.”
Common VLOOKUP Errors and Their Fixes
- #N/A: Lookup value not found in the first column. Check data and spelling.
- #REF!: The column index number is greater than the number of columns in the table array.
- Wrong Result: Using TRUE instead of FALSE when an exact match is needed.
- Data not sorted: For approximate matches, the first column must be sorted ascending.
Tips for Efficient VLOOKUP Usage
- Always lock the table array with absolute referencing ($A$2:$C$5) to avoid errors when copying formulas.
- Combine with IFERROR to handle errors gracefully, for example:
=IFERROR(VLOOKUP(E2,$A$2:$C$5,3,FALSE),”NotFound”)
- For flexible lookups when the lookup value is not in the first column, consider using INDEX-MATCH or the newer XLOOKUP (available in Excel 365).
Advanced VLOOKUP Techniques
VLOOKUP Across Worksheets
You can reference data in other sheets:
=VLOOKUP(A2,Sheet2!$A$2:$C$10,3,FALSE)
Using Named Ranges
Define named ranges for your tables to make formulas cleaner:
=VLOOKUP(lookupvalue,Employees,2,FALSE)
Real-World Applications of VLOOKUP
- Inventory Management: Find product prices, stock levels, or suppliers easily.
- Employee Data: Retrieve department, salary, or contact info from IDs.
- Financial Models: Pull data from financial statements or transaction logs.
- Student Grading: Calculate grades based on score ranges.
- Report Automation: Dynamically fetch quarterly or monthly data.
Why You Should Master VLOOKUP
VLOOKUP is a foundational Excel skill, widely used across industries. It automates tedious lookup tasks, improves data accuracy, and enhances your reporting capabilities. Many business decisions rely on fast and accurate data lookups, making VLOOKUP an indispensable tool.
Conclusion
Mastering Vlookup Excel formulas with examples makes working with data easier and more efficient. With practice, you’ll be able to confidently retrieve data, reduce manual errors, and build robust spreadsheets that serve your business or personal needs.
Start experimenting with the example formulas provided in this guide, and unlock the true power of Excel VLOOKUP in 2025!
This post (Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples ) provides a detailed understanding of VLOOKUP formula syntax, practical examples, common mistakes, and advanced uses to enable users to become proficient with this essential Excel tool.
Exercise Excel File
यह भी पढ़ें
Civil Designer: Career, Skills और Salary Guide 2025
Top 7 Essential Civil Engineering Tools Every Site Engineer Should Know
Income Tax Calculator 2024-25 in Excel (आयकर कैलकुलेटर 2024-25 एक्सेल में)
5 Simple Ways to Save Money Every Month (हर महीने पैसे बचाने के 5 आसान तरीके)


3 thoughts on “Vlookup Excel Formulas with Examples: A Complete Step-by-Step Guide for 2025”